
Practice Test: Earth and Space Science (74)
Suggested Testing Time: 4 hours
To Take This Practice Test
- Use the answer key to record your responses.
- Prefer to take it offline? You can print the questions and answer key.
Remember:
- The practice test can give you a good indication of how you may perform on an actual test, but there is no guarantee that your results will be the same as on the actual test.
- The actual test looks and operates differently than this practice test. In addition, this test includes one or more assignments that allow you to handwrite and scan your responses. Review the Testing Tutorials and Demonstrations for more information about the actual test platform.
Question 1.
Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
A quasar is a distant and extremely bright celestial object. The most powerful quasars emit more electromagnetic energy than the entire output of the Milky Way galaxy. Quasars are thought to be supermassive black holes with masses ranging from millions to billions of times the mass of the Sun. They seem to be located at the centers of galaxies and may play a role in galaxy formation.
Based on the information shown, which of the following statements best explains why quasars are the brightest of all celestial objects?
- The extremely rapid spin of a quasar energizes a surrounding cloud of dark matter, causing the dark matter to become visible and glow.
- The enormous mass of a quasar compresses surrounding clouds of hydrogen gas, causing nuclear fusion to commence and form a vast number of protostars.
- The immense distance of quasars indicates that they were formed during the Big Bang and retain the image of that enormous explosion.
- The immense gravity of a quasar attracts an enormous accretion disk of gas and dust that glows when it is accelerated as it spirals into a black hole.
Question 2.
The ability of spectroscopy to determine the composition of stars depends on the fact that:
- as elements break down in the cores of stars, subatomic particles such as neutrinos are released and escape from the stars' coronas.
- fusion reactions between different elements yield different amounts of heat and light energy.
- as elements combine to form molecules of different compounds in stars, those molecules release different wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation.
- different wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation are emitted by atoms of different elements.
Question 3.
A science teacher prepares a demonstration by stretching spandex fabric over the opening of a trash can, creating a flat, tight surface. The teacher then places a billiard ball in the center, which causes the fabric to dip under the billiard ball's weight. The teacher then rolls a marble over the fabric and it curves around the billiard ball before continuing in a different direction. This demonstration can best be used to model how:
- massive spiral galaxies merge with smaller galaxies to form an elliptical galaxy.
- light is altered as it passes near a massive object that warps space-time.
- planetary orbits are maintained by the interaction of gravity and centripetal force.
- stars are formed from the gravitational collapse of a cloud of dust and gas.
Question 4.
In 1965, two researchers detected cosmic background radiation coming from all directions in space. This discovery provided the first direct evidence of the:
- earliest formation and expansion of the universe.
- presence of black holes at the center of the Milky Way galaxy.
- massive size and homogeneity of the universe.
- bending of light by large gravitational fields.
Question 5.
An astronomer observes rapidly fluctuating radio signals from distant galaxies that occur as precisely spaced bursts of radiation. It is likely that the astronomer has located:
- an expanding planetary nebula.
- an oscillating black hole.
- a rotating neutron star.
- an eclipsing binary star system.
Question 6.
Which of the following supported the scientific conclusion that the universe began with an inflationary expansion?
- the proportion of the different elements found in asteroids
- the motion of galaxies receding from Earth in all directions
- the variation in the density of different regions of space
- the release of energy observed in nuclear fusion reactions
Question 7.
A person who is standing outside Boston, Massachusetts , at 42 degrees North latitude, at solar noon would notice that their shadow is longest on which of the following dates?
- March 21
- June 21
- September 21
- December 21
Question 8.
A planet lies in the habitable zone conducive to surface microbial life. Whether or not the planet actually can support life also primarily depends on the:
- luminosity of the star.
- planet's composition of the core.
- presence of atmospheric oxygen.
- type of galaxy in which the planet's system is located.
Question 9.
In order to illustrate the effect of Earth's axial tilt on seasonal changes, an Earth science teacher places a globe on a stand. The globe can be tilted back and forth. The teacher shines a powerful flashlight so that a circle of light is formed on the globe with the globe's vertical axis at 90 degrees relative to the flashlight beam. A student is asked to measure the diameter of the circle of light produced by the flashlight beam striking the globe. The teacher then repeats the experiment with the globe axis tilted 25 degrees toward the flashlight and 25 degrees away from the flashlight. Which of the following expressions correctly states how the diameters of the circles of light at each of the three positions are related?
- 25 degrees away position = 90 degrees position = 25 degrees toward position
- 25 degrees toward position is less than 90 degrees position is less than 25 degrees away position
- 25 degrees away position is less than 90 degrees position is less than 25 degrees toward position
- 25 degrees toward position = 25 degrees away position is less than 90 degrees position
Question 10.
Two high tides occur almost simultaneously on opposite sides of Earth. Which of the following best describes the underlying reason that a high tide occurs on the side of Earth that faces away from the Moon?
- the difference in the gravitational pull on either side of Earth
- the drag caused by frictional forces between water and the ocean floor
- the strength of the Sun's gravitational pull on ocean water
- the tilt of Earth's axis relative to the Moon's orbit
Question 11.
Which of the following explains why lunar eclipses typically occur only two or three times a year instead of each month?
- Earth's axis is tilted relative to the plane of its orbital path around the Sun.
- The time it takes Earth to orbit the Sun is much longer than the orbital period of the Moon.
- The Moon's orbital path is tilted relative to the plane of Earth's solar orbit.
- The time it takes for the Moon to orbit Earth is much longer than Earth's rotational period.
Question 12.
Which of the following statements best summarizes Newton's first law of motion as it relates to the Moon's orbit around Earth?
- The Moon's inertia keeps it moving tangent to its orbit, while Earth's gravitational field deflects it from a straight path.
- The Moon's rotation keeps it on the same path, while its velocity is maintained by Earth's gravity.
- The Moon's acceleration is driven by its mass, while its circular motion is maintained by its gravitational attraction to Earth.
- The Moon's weight causes it to fall toward Earth, while centripetal force accelerates it away from Earth.
Question 13.
Microfossils dated as early as 4 billion years ago exhibit a structure similar to bacteria found today near hydrothermal vents. These fossils support the hypothesis that life evolved near these deep-ocean structures. Which of the following statements best summarizes a primary argument that life first evolved near hydrothermal vents rather than in other Earth environments?
- Hydrothermal vents release large amounts of free oxygen created by the hydrolysis of seawater deep in Earth's crust.
- Hydrothermal vents discharge large quantities of nitrogenous compounds that could be combined to form precursors of early RNA and DNA molecules.
- Hydrothermal vents provided a steady source of energy in the form of heat when the Sun was weaker than today and provided much less energy to Earth.
- Hydrothermal vents were one of the only relatively stable environments on an Earth where most environments experienced conditions that were not favorable to life.
Question 14.
Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
During this geologic period, key events included the emergence of forests of land plants and the evolution of insects. Sea levels were high and extensive shallow seas covered large areas. In the seas, vertebrates were primarily represented by a wide array of fish. There were so many fish that this period is often called the Age of Fishes. There were cartilaginous fishes, armored fishes, lobe-finned fishes, and many types of jawless fishes.
Which of the following geologic periods is described in the information provided?
- Cretaceous
- Cambrian
- Devonian
- Triassic
Question 15.
Use the table below to answer the question that follows.
| Stratum | Species A | Species B | Species C | Species D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | common | common | blank | common |
| 2 | first appears; rare | blank | rare | common |
| 3 | blank | blank | first appears; common | first appears; common |
| 4 | common | first appears; common | blank | common |
According to the information in the table, the correct ordering of strata from oldest to youngest is represented by which of the following sequences?
- Stratum 3 is the oldest layer, stratum 4 is the second oldest, stratum 2 is the second youngest, and stratum 1 is the youngest
- Stratum 3 is the oldest layer, stratum 1 is the second oldest, stratum 2 is the second youngest, and stratum 4 is the youngest
- Stratum 3 is the oldest layer, stratum 2 is the second oldest, stratum 4 is the second youngest, and stratum 1 is the youngest
- Stratum 3 is the oldest layer, stratum 2 is the second oldest, stratum 1 is the second youngest, and stratum 4 is the youngest
Question 16.
In which of the following situations would the Law of Lateral Continuity be most important for determining the geologic history of an area?
- A large river has cut down through a stratigraphic column, leaving a deep valley and rock cliffs on either side.
- A basalt dike has intruded into a stratigraphic column and caused the constituent strata to divide into two.
- A series of strata have been eroded away and new strata have been deposited on the erosional surface.
- An anticline has caused a series of strata to bulge upward so that their orientation is tilted.
Question 17.
Which of the following topographic features in New England was created when the western edges of the African and European plates collided with the eastern edge of the North American plate?
- the coastal lowlands found throughout Rhode Island
- the presence of high quantities of granite in Massachusetts
- the layers of rock types seen in the steep walls of the Connecticut Valley
- the folded pattern of rock layers that can be seen in the Appalachian Mountains
Question 18.
A researcher investigating the geologic history of a region collects data on the orientation of a limestone layer exposed along a highway. The convention for reporting the orientation of the limestone layer typically would include which of the following pieces of information?
- the meters below the land surface of different sections of the top of the exposed part of the limestone
- the angle between an imaginary vertical line and the uppermost surface of the limestone
- the degree measurements that show the strike and dip of the bedding plane of the limestone
- the thickness of the limestone and how it has changed from its original horizontal position
Question 19.
Use the graphic below to answer the question that follows.

The top layer is breccia that lays on top of a layer of shale, then limestone, and sandstone. On the bottom right, there is a granite batholith that intrudes into the sandstone and the limestone. A fault bisects all of the layers, including the batholith and they are all shifted upwards on the right. Additionally, there is a basalt dike through the batholith, the limestone, and the shale. No overturned strata. Not to scale.
In the geologic cross section shown above, a fault has offset the geologic features exposed in the cross section. Which of the following statements about the sequence of geologic events is confirmed by the relationships in the cross section?
- The basalt dike was intruded after the faulting occurred.
- The granite batholith was intruded after the breccia was deposited.
- The fault occurred while the shale was being deposited.
- The basalt dike was intruded after the sandstone was deposited.
Question 20.
The two main sources of Earth's interior heat that drive the convection currents that cycle Earth's crust are decay of radioactive elements and heat produced by:
- tidal forces generated by the Sun and Moon acting on rocks in Earth's mantle and core.
- Earth's magnetic field acting on iron compounds scattered throughout the mantle.
- friction between Earth's rapidly spinning inner core and its liquid outer core.
- events during Earth's formation and early history.
Question 21.
Which of the following statements best explains why Earth's interior is layered with the densest material at the core?
- At one point early in its history, Earth went through a molten stage and the densest material sank to the area with the strongest gravity.
- Planetesimals that struck the Earth early in Earth's history were metallic and those that struck later were of a less dense nature.
- Convection currents within Earth's mantle continuously move less dense rocks upward and denser rocks downward.
- The rotation of Earth acts as a centrifuge and separates rocks according to their density.
Question 22.
Glacial striations in southwest Africa, southeast South America, southern India, northern Australia, and Antarctica show that portions of these continents were partially covered by large glaciers during the late Paleozoic. Which of the following statements best explains these observations?
- The southern continents were joined together and located nearer to the South Pole than they are today.
- Each of these continents raised high mountain chains that were covered in snow and ice for most of the year.
- Earth was much colder during this period than it is today, and terrain in the high latitudes of all the continents were covered by glaciers.
- Glaciers in both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres caused sea levels to fall, exposing large areas of seafloor between continents and covering them with ice.
Question 23.
As part of an introductory activity about plate tectonics, students are asked to hypothesize whether interactions along plate boundaries will result in the formation of mountain chains, ocean trenches, or horst and graben topography. In order for students to complete this activity, they must have access to which of the following data?
- the approximate size of each plate
- the rate of movement of each plate
- the direction of movement of each plate
- the locations of seismic activity on each plate
Question 24.
Seismologists first established the physical character of Earth's outer core based on the fact that:
- S waves do not pass through liquid substances.
- P and S waves are reflected from solids at different angles.
- P waves do not pass through high-temperature materials.
- P and S waves are refracted differently from irregular surfaces.
Question 25.
Studies during the 19 fifties and 19 sixties showed that the ferromagnetic minerals in ocean-floor basalts aligned with Earth's magnetic field when the basalts were still molten. This information provided evidence supporting:
- the theorized stability of Earth's rotational velocity.
- a four-billion-year-old estimate of Earth's age.
- the hypothesized liquid state of the upper mantle.
- a mechanism to help explain how lithospheric plates moved apart.
Question 26.
Which of the following are landscape features typically associated with an active strike-slip fault?
- hanging valleys and tarns
- kame terraces and eskers
- horsts and grabens
- scarps and sag ponds
Question 27.
The Atlantic Ocean began to form as a result of which of the following geologic events?
- the erosion of a plate margin from repeated continental glaciations
- the subduction of one continental plate beneath another
- the development of a large syncline east of the Appalachian Mountains
- the growth of a rift valley along a major fracture zone in the crust
Question 28.
Which of the following geologic structures is characteristic of a passive continental margin?
- a thick sedimentary platform
- an inundated forearc basin
- a complex accretionary wedge
- an active fault zone
Question 29.
A "monadnock" is notable for its isolation from other mountains and its smooth, treeless summit, which affords a panoramic view from the top. Which of the following statements best explains how monadnocks are formed?
- Monadnocks were formed when local, small, and isolated volcanoes were built up and then smoothed and shaped by erosion.
- Monadnocks were once part of a continuous terminal moraine that was cut into isolated peaks by large rivers as the glaciers melted.
- Monadnocks were once part of an old mountain chain whose softer rocks eroded away, leaving cores of harder rocks standing alone.
- Monadnocks were formed when a large sedimentary plateau was uplifted and then eroded by wind and water, leaving isolated segments freestanding.
Question 30.
An unknown mineral can scratch the standard sample of orthoclase feldspar in a Mohs test kit but cannot scratch the standard sample of quartz. The unknown mineral's hardness is most likely around which of the following values on the Mohs scale?
- 2.5
- 4.5
- 6.5
- 8.5
Question 31.
Which of the following instances of rapid erosion is an example of mass wasting?
- an avalanche
- the rapid downcutting of a mountain stream after spring snowmelt
- a landslide
- a dust storm produced by the confluence of drought and high wind
Question 32.
Use the graphic below to answer the question that follows.
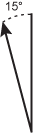
One vertical line is connected at its base to an arrow on the left that is offset from the vertical line by 15 degrees.
The map symbol shown above typically appears at the bottom of a topographic map and is known as the declination. A scientist reading the map in the field uses the declination for which of the following purposes?
- estimating the relief between two distant points on the map
- adjusting the latitude and longitude values on a flat map to account for Earth's spherical shape
- assessing the approximate distance to locations represented on the map
- determining the difference between true north as it is represented on the map and magnetic north
Question 33.
Lichens, plant roots, and fungi are able to chemically weather rock. These organisms typically accomplish this by:
- drawing molecular water from the crystals that make up the rock.
- producing acids that cause the decomposition of the rock.
- extracting minerals directly from the rock through osmosis.
- manufacturing salts that alter the rock's crystal structure.
Question 34.
Which of the following properties of water is primarily responsible for its role in mechanical weathering?
- Water increases in density as it goes from 0 degrees Celsius to 4 degrees Celsius and then decreases above 4 degrees Celsius .
- The capacity of liquid water to store heat energy is very high.
- The hydrogen bonding between water molecules gives it a high surface tension.
- Water increases in volume as it goes from a liquid to a solid state.
Question 35.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
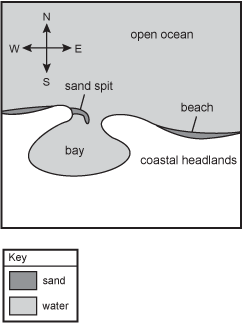
An image of an overhead view of a beach where the shore is to the south and the ocean is to the north. The west-to-east shoreline is interrupted by a bay. On the western entrance to the bay, there is a sand spit that covers half of the entrance and curves slightly south.
Which of the following statements best explains the formation of the sand spit across the entrance to the bay shown in the diagram?
- Coastal winds blowing from the east move sand from the beach to the entrance of the bay where tides alter the shape of the deposit.
- Longshore currents flowing from the west slow down and deposit sand where they cross the entrance to the bay.
- Tidal currents flowing north and south slow down and deposit sand where they flow in and out of the entrance of the bay.
- Ocean waves move the beach sand toward the west where it is carried into the entrance of the bay and modified by tidal currents.
Question 36.
Graded bedding in a sedimentary rock is an indication of which of the following depositional environments?
- desert
- high-energy beach
- marginal marine
- alluvial fan
Question 37.
Which of the following sedimentary rocks would most likely have formed from sediments accumulating in a deep-ocean trench?
- shale
- sandstone
- breccia
- limestone
Question 38.
Which of the following phenomena is best explained by the property of cohesion in water?
- Rain typically falls as discrete droplets, rather than as a fine mist.
- Rivers run in defined channels, rather than spreading out over the land.
- Water in deep lakes and oceans is layered according to density.
- Large bodies of water retain heat more efficiently than surrounding land.
Question 39.
The property of surface tension in a body of water is best illustrated by which of the following examples?
- Clouds retain their shape as they move across the sky.
- Ice forms at the edges of a lake earlier than in the lake's center.
- Water strider insects can skim across the surface of a quiet pond.
- Water flows off a mountainside after a rain in streams, rather than in sheets.
Question 40.
Use the table below to answer the question that follows.
Discharge Rate (% of normal flow)
| Hours Since a Heavy Rain | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stream 1 | 100 | 120 | 220 | 140 | 110 | 100 | 100 |
| Stream 2 | 100 | 120 | 140 | 150 | 130 | 120 | 110 |
The table shows the discharge rate as a percentage of normal flow in two streams after a heavy rain. The streams are similar in their normal discharge rates and flow over similar gradients. Which of the following statements identifies the most likely reason for the difference in discharge rates after the rainstorm between the two streams?
- The watershed for stream 1 is largely in a suburban area, while the watershed for stream 2 is largely in a forest.
- The stream bed underlying stream 1 has a higher water table than the stream bed underlying stream 2.
- The stream bed underlying stream 1 is rocky, while the stream bed underlying stream 2 is sandy.
- The watershed feeding stream 1 is more extensive than the watershed feeding stream 2.
Question 41.
Which of the following factors most influences the residence time of a molecule of water in a river?
- the mean annual volume of water in the river
- the number of tributaries entering the river
- the type of substrate the river flows over
- the overall gradient of the river
Question 42.
Higher evaporation rates from ice-free portions of the Arctic Ocean due to warmer-than-average temperatures are likely to lead to which of the following effects on other Earth systems?
- increased acidity of rain over the North American continent and higher rates of weathering of susceptible rocks
- decreased salinity of the Arctic Ocean and disruption of the deep circulation of water within the Arctic Circle
- decreased winter snowfall associated with higher rainfall in Siberia and consequent increasing of regional albedo
- increased snowfall in Southern Canada and extensive spring flooding in the central United States plains
Question 43.
As climate change results in higher global temperatures, mountain glaciers around the world are melting and diminishing in size. Which of the following statements best describes an effect of this phenomenon on other Earth systems?
- As the glaciers retreat, dark rocks and open water are exposed, which lowers the albedo of the surface, causing it to absorb and retain more heat and melt more ice and snow.
- Water vapor evaporated from the surface of glaciers forms clouds that move downslope and increase precipitation over deserts on the leeward of the mountains.
- Sudden release of large amounts of water from melting glaciers creates floods that excavate canyons from the edge of the glaciers to the base of the mountains.
- Water vapor evaporated from the surface of glaciers lingers over mountaintops and absorbs heat from the Sun, which melts more ice and snow.
Question 44.
For the past ten years, a scientist has been studying the effects of acid rain on five lakes that are located downwind of a large coal-fired power plant. Over this time period, which of the following differences between the five lakes is most likely to be an independent variable in the study?
- the average pH of the rivers feeding the lakes
- the strata underlying the lakes' watersheds
- the average water clarity of the lakes
- the biodiversity among the lakes
Question 45.
Hydrologists are helping establish the variability of discharge on a particular river. They determine the average discharge of the river over the past 100 years using historical data. Which of the following is the best measure of the variability of this data set?
- the median
- the standard deviation
- the mode
- the arithmetic mean
Question 46.
Water in its solid form is less dense than water in its liquid form. This characteristic is primarily a result of the:
- rigid three-dimensional structure of ice that keeps water molecules from getting too close to each other.
- high viscosity of liquid water that makes its molecules more closely packed than other liquids.
- internal kinetic energy of ice that keeps the molecules in ice relatively far apart due to their rapid vibration.
- high heat capacity of liquid water that allows it to store energy with only a small change in volume.
Question 47.
The High Plains Aquifer extends from South Dakota to central Texas. Since the early 19 hundreds , the surface of the aquifer has dropped significantly in parts of Texas, Oklahoma, and Kansas. This change in the aquifer is primarily due to which of the following?
- a reduction in forest cover from logging that has increased evaporation rates from exposed soils overlying the aquifer
- a shift in climate conditions during the past 100 years that has reduced the water available for aquifer recharge
- the compaction of soils from mechanized farming that has reduced the permeability of soils overlying the aquifer
- the withdrawal of water for agricultural use that has been greater than the aquifer's recharge rate from precipitation
Question 48.
Which of the following ocean surface water masses is likely to have the greatest density?
- cold and relatively high salinity waters of the North Atlantic Ocean
- warm and high salinity waters of the Caribbean Sea
- cold and moderately saline waters of the equatorial eastern Pacific Ocean
- warm and low salinity waters of the South China Sea
Question 49.
In recent years, scientists have documented a drop in the salinity of the North Atlantic Ocean. The primary concern of scientists studying this phenomenon is that a large drop in the salinity of North Atlantic water would affect the:
- acidity of the surface water in one of the world's most important fisheries.
- amount of precipitation in the temperate latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere.
- rate at which heat is transferred northward by the Gulf Stream.
- formation of sea ice in a region already under stress from climate change.
Question 50.
The movement of deep-ocean currents is driven primarily by which of the following?
- the transfer of surface wave energy through friction
- gravitational effects of the Moon
- the orbit and rotational motion of Earth
- temperature and salinity gradients
Question 51.
Which of the following statements best explains why temperatures increase with altitude in the stratosphere?
- Heavy clouds in the lower stratosphere reflect incoming solar radiation back up into the upper levels of the stratosphere.
- High winds traverse the lower stratosphere and cool it by convection, but the air in the upper levels of the stratosphere is still.
- Ozone breakdown high in the stratosphere produces atomic and molecular oxygen, which release heat when they recombine into ozone.
- Incoming solar radiation is more intense in the upper levels of the stratosphere because it is not blocked by the thin air of the mesosphere.
Question 52.
Which of the following statements best explains why a greater percentage of ultraviolet B (UVB) and ultraviolet C (UVC) radiation is blocked by the ozone layer than ultraviolet A ( U V A ) radiation?
- The efficiency with which ozone blocks ultraviolet light varies throughout the electromagnetic spectrum, and UVB and UVC photons occupy energetic bands that are more efficiently absorbed than U V A photons.
- The energy of ultraviolet light splits oxygen molecules in the oxygen-ozone cycle, and high-energy UVB and UVC photons are more effective at this than lower-energy U V A photons.
- UVB and UVC photons have lower energy and longer wavelengths and so travel more slowly than U V A photons, which means they spend a longer period of time traversing the ozone layer and are therefore more likely to be deflected.
- UVB and UVC photons are much more common in sunlight than are U V A photons, which means that a higher percentage of them are absorbed by the ozone in the ozone layer.
Question 53.
Most incoming infrared radiation is blocked by atmospheric water vapor because when an infrared photon strikes a water vapor molecule, its energy:
- breaks the bonds between the atoms in the water molecule, creating free oxygen.
- strips electrons away from the oxygen atoms in the water molecule.
- is reflected back into space by the crystal lattice of the water molecule.
- causes the atoms in the water molecule to vibrate.
Question 54.
Radiation, evaporation, and convection are more significant processes of heat exchange between the ocean and the atmosphere than conduction because conduction can only take place:
- where the surface of the ocean and the overlying air are completely still.
- at a thin layer of the ocean's surface where molecules of water and molecules of air are in contact.
- when the temperatures of the ocean's surface and the overlying air are the same.
- between molecules of the same substance, so it is limited to heat transfer between ocean water molecules and water vapor in the air.
Question 55.
Which of the following factors is the ultimate cause for the generation of prevailing surface winds?
- variation in the concentrations of water vapor in the lower troposphere
- differences in the speed of Earth's rotation at different latitudes
- pressure changes from the surface to the upper troposphere
- uneven heating of the Earth's surface and lower atmosphere
Question 56.
The increasing action of which of the following processes contributes to a positive feedback mechanism in Earth's climate?
- weathering of rocks on continents
- glacier ice melting
- carbon dioxide dissolving in the oceans
- water condensation
Question 57.
A high school teacher plans to do a lesson demonstrating the relationship between storms, pressure, and air during a unit on atmosphere and atmospheric processes. Which of the following concepts would be most useful in the students' understanding of this lesson?
- kinetic molecular theory
- heat transfers
- laws of thermodynamics
- greenhouse effect
Question 58.
The significant increase of which of the following interactions between Earth systems has the greatest potential to indirectly cause a rise in sea level?
- deforestation of tropical regions, reducing carbon sequestration by the biosphere
- pollution of coastal waters with agricultural runoff, triggering algal blooms
- eruption of low-latitude volcanoes, producing a change in atmospheric chemistry
- desertification of semi-arid lands, generating wind-blown dust in the troposphere
Question 59.
Carbon is cycled through the atmosphere, the hydrosphere, the biosphere, and the lithosphere. Which of the following describes one step in the movement of carbon from the atmosphere to the lithosphere?
- the production of carbonic acid from limestone during weathering
- the extraction of bicarbonate ions from seawater during coral reef formation
- the formation of carbon dioxide during the decay of biomass
- the absorption of atomic carbon in seawater by deep-ocean sediments
Question 60.
Which of the following statements explains why the sky appears blue?
- Air molecules selectively scatter the shorter wavelengths of visible light.
- Air molecules reflect the longer wavelengths of visible light.
- Water vapor refracts visible light into its component frequencies.
- Water vapor selectively absorbs visible light at certain wavelengths.
Question 61.
Overcast nights tend to be warmer than clear nights even when temperatures on the preceding day have been the same. This is primarily because on overcast nights:
- evaporation rates are substantially reduced.
- clouds radiate infrared energy downward.
- convection currents are unable to develop.
- water vapor condenses, releasing energy.
Question 62.
As a result of the Coriolis effect, wind currents tend to:
- cool off as they converge and rise.
- flow in a straight path as they cross lines of longitude.
- heat up as they diverge and sink.
- curve as they flow over Earth's surface.
Question 63.
Which of the following data for a specific city provides information about weather rather than climate?
- the average snowfall for each month over the last 10 years
- the date of the first killing frost in autumn over the last 30 years
- the amount of precipitation that fell during a recent severe rainstorm
- the number of days in a year with temperatures over a certain value
Question 64.
After a discussion of the causes and effects of climate change, a teacher overhears one student say to another student, "Last week, we got 10 inches of snow and the temperature went down to 5 below zero." Then, the student directs a question at the teacher, "How could the world be warming?" The teacher could most appropriately respond to the student's question by explaining that:
- climate change data are difficult to collect and understand by the non-specialist, while weather-related data are easy to collect and understand by everyone.
- the effects of climate change are poorly known and can't be predicted, but weather can be predicted days ahead of time using time-tested methods.
- climate change data can provide information about likely changes in expected weather over time, but they cannot accurately predict day-to-day weather events.
- the effects of climate change on weather can vary from state to state and it is likely that such effects will be minimal in the students' area.
Question 65.
Which of the following statements best describes how a temperature inversion typically forms in the lower levels of the troposphere?
- A stationary warm air mass rises in place in winter and the air below is cooled by contact with the surface.
- A stationary cold air mass in summer is warmed by contact with the ground and cools as it rises.
- A cold air mass is forced upward by another cold air mass and warms as it rises.
- A warm air mass sits above a cold air mass, whose movement is blocked by topography.
Question 66.
A mass of warm air is rapidly forced upward when it is caught between a warm front and a rapidly advancing mass of cold air. These events will most likely lead to which of the following types of weather in the region?
- partly sunny skies, puffy fair-weather clouds, moderate temperatures, and low humidity
- sunny skies, cool temperatures, and calm winds
- strong winds and heavy precipitation, with possible thunderstorms and tornadoes
- heavy, low-level clouds, drizzle, and high humidity
Question 67.
Which of the following climate zones exhibits the least seasonal variation in temperature and precipitation?
- humid continental zone
- semiarid zone
- humid subtropical zone
- tropical wet zone
Question 68.
As part of a unit on climatic regions, a teacher provides students with a bar graph comparing mean annual temperature and rainfall data for five broad climatic regions. Which of the following additional resources should the teacher provide to help students understand the differences between these regions and their effect on the associated biomes?
- a histogram comparing the average annual rainfall and temperature for each region for the last five years
- two scatter plots, one showing the maximum and one showing the minimum annual temperature for each region
- a circle graph showing average annual rainfall for each region as a percent of the total for all five regions
- five separate line graphs, one for each region, showing the average monthly rainfall and temperature for each region
Question 69.
A scientist collects 50 years of temperature data from the Midwest that show a steady increase in daytime summer temperatures. Which of the following is the best way for the scientist to use these data to make predictions about how the average temperatures may increase in the coming years?
- Plot the data set and extend the line of best fit into the coming years.
- Take the median of the data set and add that to the average temperature for each coming year.
- Determine the range of the data set and assume any future increases will be within that range.
- Calculate the total change over time in the data set and assume it reflects the minimum increase in the future.
Question 70.
Use the graphic below to answer the question that follows.
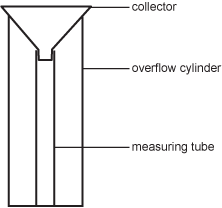
A large, funnel-shaped collector rests on top of a measuring tube that is the center of an overflow cylinder.
The standard rain gauge shown above has a long, narrow measuring tube and a funnel-shaped collector at the top. The area of the top of the collector is 10 times greater than that of the measuring tube. This difference between the cross-sectional area of the measuring tube and the collector is designed to:
- ensure that the rainfall measured represents a realistic average.
- reduce the effect of wind on rainfall accumulation.
- minimize the amount of splashed rainwater that can enter the device.
- provide a more precise measurement of total rainfall.
Question 71.
An occluded front typically forms under which of the following conditions?
- A wedge of cool air between two warm fronts is forced upward as one of the fronts overtakes the other.
- A cold front catches up with a warm front, forcing warm air between the fronts upward and producing rain.
- A wedge of cold air between two warm fronts is forced upward as one of the fronts overtakes the other.
- A cold front overrides another cold front, trapping warm air at the surface and producing rain.
Question 72.
Which of the following climate characteristics is the primary factor controlling the type of vegetation in the prairie of the upper Midwest?
- strong seasonal winds
- limited annual precipitation
- regular grass fires
- temperature extremes
Question 73.
Use the graph below to answer the question that follows.
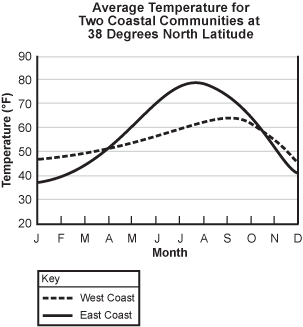
A graph of average temperature over the course of a year. The X axis indicates the month of the year starting in January and the y-axis indicates the average temperature. The trend line representing the West Coast starts at around 48 degrees Fahrenheit and slowly increases to around 63 degrees Fahrenheit in September before dropping back down to 48 degrees in December. The East Coast trendline begins at around 38 degrees Fahrenheit and increases more rapidly to a peak of around 80 degrees Fahrenheit in August before rapidly decreasing to around 40 degrees Fahrenheit in December.
The graph shows the average temperature over the course of a year in a West Coast community and an East Coast community at 38 degrees north latitude. Which of the following is the most significant factor responsible for the difference between the patterns of temperature change of the two coastal locations over the course of the year?
- the inland topography adjacent to the two locations
- the amount of precipitation at different times of the year
- the direction of large-scale winds throughout the year
- the moderating effect of near-shore waters in each location
Question 74.
Fossil evidence indicates that tropical conditions once existed across the United States during the late Paleozoic era. This difference in the climate of North America today and the climate during the Paleozoic era was caused primarily by changes in the:
- concentration of oxygen in the atmosphere.
- intensity of solar radiation.
- directions in which ocean currents flow.
- positions of the continents.
Question 75.
Under which of the following conditions is advection fog most likely to form?
- Cold air becomes trapped beneath a layer of warmer air.
- Hot dry air in contact with the surface cools after sunset.
- Cool moist air warms as it flows down a mountain side.
- Warm moist air flows over cold ocean water.
Question 76.
Which of the following types of environmental damage is most likely to occur when natural gas supplies are transported by pipeline?
- large wildfires
- habitat disruption
- pollution of groundwater
- acidification of surface water
Question 77.
The limitations on the functional life of hydroelectric dams for generating electricity in the short term is largely a result of:
- reduced annual precipitation due to the effects of the reservoir on the local climate.
- reduced flow of rivers feeding the reservoir due to degradation of the watershed.
- reduced capacity of the reservoir due to sediment deposition.
- reduced volume of the reservoir due to evaporation.
Question 78.
Which of the following is the best example of a hidden cost of the use of fossil fuels for electricity generation?
- high maintenance expenses for fossil fuel-powered generating plants
- expenses for transporting fossil fuels from where they are extracted to the generating plant
- federal and state government subsidies paid to fossil fuel companies
- health problems from exposure to pollutants produced by fossil fuel-powered generating plants
Question 79.
A relatively new method for managing timber production is to clear-cut relatively small patches within a forest, leaving the surrounding forest undisturbed. Which of the following statements describes a positive effect of this practice on the forest?
- It reduces the spread of insect pests in the parts of the forest that were not logged.
- It provides shelter for small animals in the area left behind in the forest sections that were logged.
- It increases infiltration of water into the soil by removing sources of low transpiration rates in the forest.
- It increases habitat diversity by opening parts of the forest to sunlight, which encourages growth of early successional plants.
Question 80.
Irrigation agriculture is, by far, the biggest user of scarce water in parts of California and the Southwest. Which of the following strategies is likely to be most practical and effective for reducing the amount of water used for irrigation of crops in these regions?
- replacing sprinkler, central pivot, and flood methods of irrigation with drip irrigation and switching to crops that can be irrigated in this manner
- waiting until crops in the field show signs of slowed growth and water stress before irrigating and then irrigating to resume growth
- using sprinklers to water crops thoroughly and replacing current crops with ones that are well adapted to extremely arid conditions
- reducing the density of plants in every field and abandoning the fields that require irrigation to produce a viable crop
Question 81.
Due to its relationship to many factors, data on which of the following characteristics would allow the best assessment of surface water quality?
- water temperature
- water pH and amount of dissolved oxygen
- amount of pollutants visible in the water column
- type of organisms present in the water and under rocks
Question 82.
A scientist is investigating monthly variation in the amount of carbon released into the atmosphere from a power plant. Calculating which of the following statistics for monthly emissions would allow the most valid comparison among months for these data?
- mode
- median
- mean
- range
Question 83.
Economically valuable minerals, such as gold and silver, are often found in the country rock surrounding large plutons. The formation of these types of minerals under these conditions is commonly the result of:
- isostatic readjustment.
- magmatic differentiation.
- hydrothermal alteration.
- chemical weathering.
Question 84.
Which of the following organisms is most responsible for fixing atmospheric carbon dioxide to create organic molecules?
- coral polyps
- bacteria
- phytoplankton
- protozoa
Question 85.
Which of the following characteristics of a pyroclastic flow from the eruption of a stratovolcano makes it much more dangerous than a lava flow from an eruption of a shield volcano?
- the inclusion of ash within the pyroclastic flow
- the much faster speed of the pyroclastic flow
- the much hotter temperature of the pyroclastic flow
- the inclusion of pieces of rock within the pyroclastic flow
Question 86.
Global climate change is having significant negative effects on human populations across the world. Which of the following effects of global climate change is likely to directly cause the most severe disruption of global human food supplies?
- changes in precipitation patterns
- increased severity of storms
- spread of invasive species
- rise in sea levels
Question 87.
Which of the following statements best explains how major eruptions of stratovolcanoes can have global effects on human populations for several years?
- They release sufficient gases, such as carbon dioxide, to cause a spike in global temperatures and associated increase in severe weather events.
- They release toxic gases that rise into the jet stream and are dispersed worldwide, causing an increase in respiratory illness.
- They release clouds of ash that react with sunlight to produce acid precipitation, causing disruption of aquatic ecosystems.
- They release aerosols, such as sulfur dioxide, that lower global temperatures and disrupt crop production.
Question 88.
Tiltmeters are used to provide early warning of volcanic eruptions primarily by assessing which of the following factors?
- viscosity of the magma
- swelling of the magma chambers
- paths of likely lava flow
- minor earthquakes around the volcano
Question 89.
A Global Positioning System (GPS) and Doppler radar would be most useful for providing which of the following types of information about a tornado in real time?
- the likelihood that a tornado will touch down
- the maximum wind speeds reached in the tornado's center
- the path that a tornado is likely to take
- the period of time during which a tornado is likely to develop
Question 90.
Which of the following factors was responsible for rapid global warming during Earth's prehuman history?
- outgassing of carbon dioxide by numerous large-scale volcanic eruptions
- uplift of continental mountain ranges due to collisions of tectonic plates
- release of methane from ocean-floor deposits of methane hydrate crystals
- burial of plants in extensive swamps leading to the formation of coal beds
Question 91.
In developing earthquake-resistant structures, engineers should emphasize solutions that minimize the effect of which of the following types of stresses?
- compressive
- torsional
- shear
- tensional
Question 92.
A climatologist is investigating the causes of an extended drought in a particular region. Which of the following questions would provide the best foundation for the climatologist's investigation into the causes of the drought?
- How could the drought conditions in the region best be managed?
- What variables affect the region's precipitation during droughts?
- How long did other droughts in the region last?
- Why do droughts strike only in certain regions and not others?
Question 93.
The broad shape and gentle slope of Hawaiian volcanoes are, to a great extent, a result of the erupted magma's:
- high gas content.
- mafic composition.
- low iron content.
- felsic composition.
Question 94.
Ocean acidification due to increased absorption of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere has which of the following direct effects on marine organisms?
- increasing the availability of nitrogen and phosphorus, which fuels the explosive growth of some forms of phytoplankton
- decreasing the availability of calcium carbonate, which interferes with the ability of some organisms to form shells and skeletons
- increasing the levels of oxygen concentration in seawater, which increases the ability of mature individuals of large species of fish to breathe
- decreasing the availability of carbon dioxide in seawater, which raises the primary productivity of phytoplankton by increasing their ability to photosynthesize
Question 95.
Increase in global temperatures due to the release of greenhouse gases has certain effects on the lithosphere. Which of the following conditions is likely to most significantly increase climate change in the future?
- greater weathering of limestone, which will lead to increased release of carbon dioxide
- greater erosion of topsoil, which will lead to a reduction in its water-holding capacity and increased atmospheric water vapor
- greater thawing of the Arctic permafrost, which will lead to increased release of methane gas
- greater humidity in tropical forests, which will lead to increased release of carbon dioxide from rapid decay of soil organic matter
Question 96.
A scientist is investigating the source of a petroleum contaminant in a high-yield drinking-water well. The well is deep and draws from a confined aquifer. Test wells drilled immediately to the north and to the east of the well are found to be contaminated. Test wells drilled to the south and west are not. The scientist concludes that the contaminant must be coming from the north and east. Which of the following factors would most reduce the validity of the scientist's conclusion?
- The contaminated test wells are on the up-gradient side of the drinking-water well where groundwater in the confined aquifer flows toward the well.
- The uncontaminated samples were collected when the pump for the drinking-water well was on, while the other samples were collected when it was off.
- The contaminated samples were collected on the same day by different people.
- The uncontaminated test wells were drilled to a depth that is above the confined aquifer supplying water to the drinking-water well.
Question 97.
A researcher is analyzing data collected for a study of climate change. Which of the following actions by the researcher would most strongly bias the analysis?
- noting flaws in the research design that may have generated faulty data
- removing data that significantly differ from expected results
- altering the graphical presentation of the data set to make it more readable
- summarizing data collected on a daily basis into a weekly average
Question 98.
Media accounts of major hurricanes often mention a growing concern that global warming will increase the frequency of major hurricanes affecting the United States. Most climatologists are uncomfortable with this kind of statement from the media primarily because it is:
- a generalization that does not accurately reflect the complexity of research on the topic.
- an unsubstantiated rumor without any support in the broader scientific community.
- a government issue that only official agencies should address to avoid unnecessarily scaring the public.
- an unethical strategy for selling news that may cause disruption to the larger economy.
Question 99.
Climatologists have used computer models to investigate possible consequences of increased average global temperatures on various Earth systems. According to the models, which of the following changes in an Earth system is likely to occur in association with an increase in average global temperatures?
- Regions prone to drought will become drier, due to longer periods without adequate rainfall.
- Jet stream winds will shift position more frequently, causing rapid changes in weather conditions.
- Hurricanes will become less common in tropical areas, due to a strengthening of the Coriolis effect.
- El Niño events will occur at longer intervals, causing anomalous weather conditions to last longer.
Question 100.
Which of the following is an effective way to reduce the acid precipitation resulting from power plant emissions?
- reacting sulfur dioxide with calcium hydroxide by forcing exhaust through a spray of lime and water
- filtering the dust particles generated by the breakdown of coal through fine mesh filtration systems
- converting carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide with smokestack catalytic converters
- removing volatile hydrocarbon compounds found in coal before the fuel is burned
Open-Response Items
The directions shown below represent what you will see on the actual test. For the purposes of this practice test, you will be able to type your written responses in the boxes provided on the answer key.
This section of the test consists of two open-response item assignments. You will be asked to prepare a written response of approximately 150 to 300 words, or 1 to 2 pages, for each assignment.
Read the assignments carefully before you begin your responses. Think about how you will organize your responses. You may use the erasable sheet(s) to make notes, write an outline, or otherwise prepare your responses. However, your final response to each assignment must be either:
- typed into the on-screen response box,
- written on a response sheet and scanned using the scanner provided at your workstation, or
- provided using both the on-screen response box (for typed text) and a response sheet (for calculations or drawings) that you will scan using the scanner provided at your workstation.
Instructions for scanning your response sheet(s) are available by clicking the "Scanning Help" button at the top of the screen.
As a whole, your response to each assignment must demonstrate an understanding of the knowledge of the field. In your response to each assignment, you are expected to demonstrate the depth of your understanding of the subject area by applying your knowledge rather than by merely reciting factual information.
Your response to each assignment will be evaluated based on the following criteria.
- Purpose: the extent to which the response achieves the purpose of the assignment
- Subject Knowledge: appropriateness and accuracy in the application of subject knowledge
- Support: quality and relevance of supporting evidence
- Rationale: soundness of argument and degree of understanding of the subject area
The open-response item assignments are intended to assess subject knowledge. Your responses must be communicated clearly enough to permit valid judgment of the evaluation criteria by scorers. Your responses should be written for an audience of educators in this field. The final version of each response should conform to the conventions of edited American English. Your responses should be your original work, written in your own words, and not copied or paraphrased from some other work.
Be sure to write about the assigned topics. Remember to review your work and make any changes you think will improve your responses.
Any time spent responding to an assignment, including scanning the response sheet(s), is part of your testing time. Monitor your time carefully. When your testing time expires, a pop-up message will appear on-screen indicating the conclusion of your test session. Only response sheets that are scanned before you end your test or before time has expired will be scored. Any response sheet that is not scanned before testing ends will NOT be scored.
Question 101.
Use the information below to complete the assignment that follows.
Phenomenon
Stars undergo change in the production of energy and elements over the course of their life cycles.
Student Standard
HS- E S S 1-1: Use informational text to explain that the life span of the Sun over approximately 10 billion years is a function of nuclear fusion in its core. Communicate that stars, through nuclear fusion over their life cycle, produce elements from helium to iron and release energy that eventually reaches Earth in the form of radiation.1
Assignment
Use your knowledge of the relationship between the life cycle of stars and their production of energy and elements to write a response of approximately 150 to 300 words, or 1 to 2 pages, in which you:
- describe the key scientific concepts related to the physical laws of the universe that govern the life cycle of stars to the depth of knowledge a student would need to master standard HS- E S S 1-1;
- include a representative graph, formula, and/or diagram with labels to model the reactions that occur in stars, resulting in the production of elements; and
- discuss how an Earth and space science teacher could use the specific science and engineering practice of "developing and using models" to help students understand phenomena related to stellar evolution.
1 2016 Massachusetts Science and Technology/Engineering Curriculum Framework. Massachusetts Department of Elementary and Secondary Education.
Question 102.
Use the information below to complete the assignment that follows.
Experimental Design Objective
Design an investigation that addresses the interactions between Earth's hydrosphere and other Earth systems.
Student Standard
HS- E S S 2-2: Analyze geoscience data to make the claim that one change to Earth's hydrosphere can create feedbacks that cause changes to other Earth systems.2
Assignment
Use your knowledge of Earth science to write a response of approximately 150 to 300 words, or 1 to 2 pages, in which you:
- form and describe a testable scientific claim that addresses the relationship between ground vegetation, water runoff, and soil erosion to the depth of knowledge a student would need to master standard HS- E S S 2-2;
- outline a specific scientific procedure to investigate the proposed claim, including identifying variables, controls, and safety procedures;
- explain how any collected data may provide evidence that supports or refutes the proposed claim; and
- discuss how an Earth and space science teacher could use the specific science and engineering practice of "analyzing and interpreting data" to help students understand the hydrosphere's influence on other Earth systems.
2 2016 Massachusetts Science and Technology/Engineering Curriculum Framework. Massachusetts Department of Elementary and Secondary Education.