Test Information Guide
Overview of the Tests
The Massachusetts Tests for Educator Licensure (MTEL) program includes a Communication and Literacy Skills test, PreKindergarten to grade 12 subject matter tests, a Vocational Technical Literacy Skills Test, and an Adult Basic Education test. See www.mtel.nesinc.com for a complete list of MTEL tests currently offered. Information on what tests must be taken may be obtained from the Massachusetts Department of Elementary and Secondary Education's website, www.doe.mass.edu/mtel/.
All tests included in the program are criterion referenced; that is, they are designed to measure a candidate's knowledge in relation to an established standard of competence (criterion) rather than in relation to the performance of other candidates. Each MTEL test is also objective-based; that is, it is based on content stated in a set of test objectives for the test field. The purpose of the tests is to help identify those candidates who have the appropriate level of knowledge and skills judged to be important for educators in Massachusetts public schools.
The MTEL tests are explicitly aligned with the relevant Massachusetts licensure regulations and the state's standards in the Massachusetts curriculum frameworks. These documents are available at www.doe.mass.edu/mtel/; the MTEL test objectives are available at www.mtel.nesinc.com.
Description of the Tests
Most tests in the MTEL program include both multiple-choice and open-response test items. The number of multiple-choice and open-response test items varies across the tests. Refer to the table below for information about types and numbers of test items on each type of test.
| Test Type | Test Description |
|---|---|
Communication and Literacy Skills |
Reading subtest This subtest includes 35 multiple-choice items, seven (7) short-answer sentence correction items, and two open-response items—a summary exercise and a composition exercise. The summary exercise requires candidates to spend about 20–30 minutes to prepare an adequate response; the composition exercise requires candidates to spend about 45–60 minutes to prepare an adequate response. The multiple-choice and short-answer item section counts for 50 percent of the candidate's score, the summary exercise counts for 15 percent of the candidate's total test score, and the composition exercise counts for 35 percent of the candidate's total subtest score. |
CASA (alternative to the Communication and Literacy Skills test) |
Reading subtest This subtest includes 42 multiple-choice items and 1 constructed-response assignment. The multiple-choice section counts for 60 percent of the candidate's total subtest score, and the constructed-response assignment section counts for 40 percent of the candidate's total subtest score. |
Essential Academic Skills (alternative to the Communication and Literacy Skills test) |
Subtest I This subtest includes 36 multiple-choice items and 1 written assignment. The multiple-choice section counts for 75 percent of the candidate's total subtest score, and the written assignment section counts for 25 percent of the candidate's total subtest score. |
MoGEA (alternative to the Communication and Literacy Skills test) |
Reading Comprehension and Interpretation subtest This subtest includes 1 written assignment. The written assignment section counts for 100 percent of the candidate's total subtest score. |
WEST–B (alternative to the Communication and Literacy Skills test) |
Reading subtest This subtest includes 50 multiple-choice questions and 2 constructed-response questions. |
MTEL-Flex Assessments |
MTEL-Flex provides an assessment option for MTEL candidates whose score on select MTEL test fields is within one standard error of measurement to the passing score (for more information about eligibility for MTEL-Flex, candidates should review the relevant MTEL-Flex assessment page). Candidates must have achieved this score on the currently operating version of the test after the approval of the regulatory pilot to explore alternatives to the MTEL, which was approved by the Board of Elementary and Secondary Education on October 20, 2020 |
|
Subject Matter Tests |
These subject matter tests include 100 multiple-choice items and two open-response items requiring candidates to spend about 20–30 minutes each to prepare an adequate response. The multiple-choice section counts for 80 percent and the open-response section counts for 20 percent of the candidate's total test score. |
|
Subject Matter Tests |
These subject matter tests include 85 multiple-choice items and two open-response items requiring candidates to spend about 20–30 minutes each to prepare an adequate response. |
|
Subject Matter Test |
Multi-subject subtest Mathematics subtest |
|
Subject Matter Test |
This subject matter test includes 60 multiple-choice items and one open-response item consisting of five parts. The open-response item requires candidates to spend about 20–30 minutes to prepare an adequate response to each of the five parts of the assignment, for a total of about |
|
Subject Matter Test |
This subject matter test includes 100 multiple-choice items. The multiple-choice section counts for 100 percent of the candidate's total test score. |
|
Language Subject Matter Tests |
French and Spanish
Chinese (Mandarin), German, Italian, Portuguese, and Russian |
Adult Basic Education |
This subject matter test includes 100 multiple-choice items and two open-response items requiring candidates to spend about 20–30 minutes each to prepare an adequate response. The multiple-choice section accounts for 85 percent and the open-response section counts for 15 percent of the candidate's total test score. |
Vocational Technical Literacy Skills Test |
Reading subtest
Writing subtest |
Development of the Tests
The development process for the Massachusetts Tests for Educator Licensure involves numerous steps. During the development of the test objectives, the Massachusetts Regulations for Educator Licensure and Preparation Program Approval, the Massachusetts curriculum frameworks, and other key state and national documents were consulted. Massachusetts educators participated throughout the development process. The objectives for each test field were reviewed and validated by an advisory panel of licensed and practicing Massachusetts public school educators and higher education institution faculty. A content validation survey was conducted using randomly sampled, practicing Massachusetts public school educators and higher education institution faculty members in educator preparation programs and in the arts and sciences. Each survey participant reviewed the test objectives in his or her field to ensure that the objectives are important to the job of a Massachusetts educator and reflect the subject matter knowledge necessary for entry-level teaching in Massachusetts public schools. The test items were aligned with both the test objectives and the educational materials relevant to Massachusetts, including the state's licensure regulations and the curriculum frameworks. The test items were reviewed and verified by Massachusetts educators for inclusion on the test.
An individual's performance on a test is evaluated against an established standard or qualifying score. The qualifying score for each test is established by the Massachusetts Commissioner of Elementary and Secondary Education and is based in part on the professional judgments and recommendations of Massachusetts educators. Candidates who do not achieve the qualifying score on a test may retake it. Candidates who have met the qualifying score on a test are not required to retake it.
Structure of the Tests
While the content covered by each test in the MTEL program is different, the structure that underlies the content of the tests is similar. In general, the structure is as follows:
- The content of each subject matter test field is organized into three to nine subareas. These subareas define the major content domains of the test.
- Each subarea includes one or more test objectives. The test objectives are broad, conceptual statements, written in language that reflects some of the skills, knowledge, and understanding that an educator needs in order to teach the test field in Massachusetts public schools.
- Each test objective is clarified and further described by a descriptive statement, providing examples of the types of content covered by the test objective.
- Each multiple-choice item is written to assess understanding of a test objective.
- Each open-response item is written to assess understanding of one or more test objectives.
- The number of test objectives within a given subarea generally determines the proportion of multiple-choice items that will address that subarea on a test. In other words, subareas with a greater number of test objectives will generally receive more emphasis (i.e., have a greater number of corresponding multiple-choice items) on the test than those with fewer test objectives. The number of test items and subarea proportions for each MTEL test are indicated in the Test Overview Chart found in this guide.
The chart below illustrates the relationship among subareas, test objectives, descriptive statements, and test items in a typical test field.
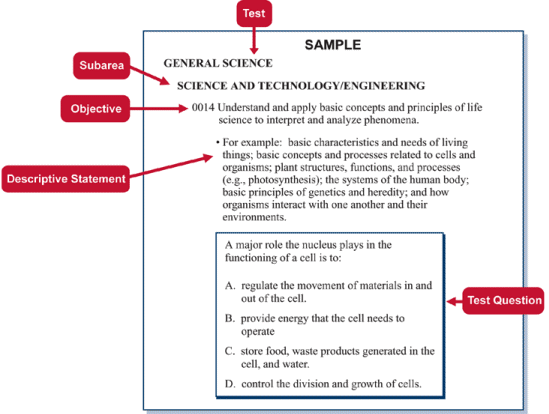
SAMPLE
Test
General Science
Subarea
Science and Technology/Engineering
Objective
0014 Understand and apply basic concepts and principles of life science to interpret and analyze phenomena.
Descriptive Statement
For example, basic characteristics and needs of living things; basic concepts and processes related to cells and organisms; plant structures, functions, and processes (e.g., photosynthesis); the systems of the human body; basic principles of genetics and heredity; and how organisms interact with one another and their environments.
Test question
A major role the nucleus plays in the functioning of a cell is to:
- regulate the movement of materials in and out of the cell
- provide energy that the cell needs to operate
- store food, waste products generated in the cell, and water
- control the division and growth of cells